Overview of dyslexia
People with dyslexia process information differently, which generally results in difficulties with reading and spelling. They may take longer to process information (both spoken and written). In addition, their difficulties with working memory make it harder for them to retain and manipulate information. On the plus side, many people with dyslexia are creative, ‘big picture’ thinkers with strong visual skills.
Common challenges faced by students with dyslexia
- Keeping up in lectures and taking accurate, concise notes.
- Maintaining concentration in lectures and when reading.
- Extracting the main points from lectures and texts, especially if abstract or complex.
- Working out what assignment briefs mean and how to tackle them.
- Getting their ideas down on paper in a logical, well-structured way.
- Phrasing their ideas clearly and concisely.
- Proof reading their writing for mistakes in spelling, punctuation and grammar.
- Completing reading and writing tasks as quickly as their peers.
- Organising their time and meeting deadlines.
- Remembering appointments and tasks.
- Responding quickly to spoken questions in seminars and discussions.
- Demonstrating their full potential in exams.
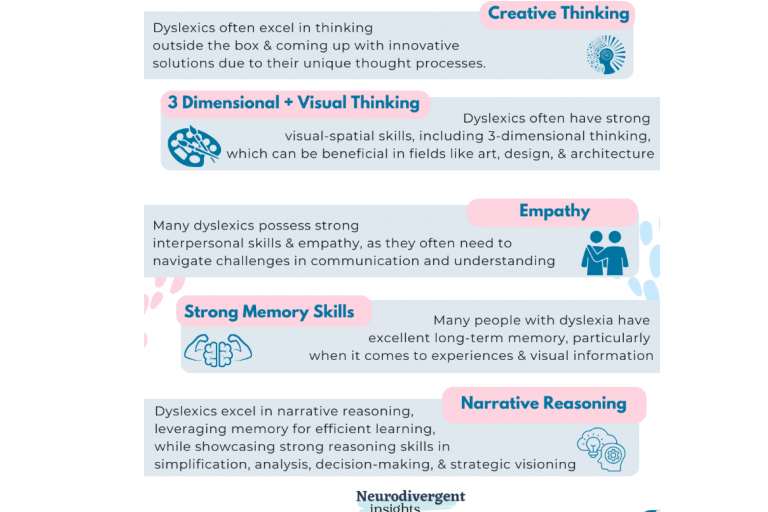
Dyslexic strengths and challenges
This blog post from psychologist Dr. Megan Neff explores different types of dyslexia, some challenges and some strengths.

Screening checklists
Download this Adult Dyslexia Checklist from the British Dyslexia Association or read about the Signs of dyslexia here.
Alternatively, check out this Adult Reading History Questionnaire from the International Dyslexia Association.

Top tips
Useful tips for college and university students. As well as tips, there are some suggested technology tools.
See also this 'Top Tips for Adults with Dyslexia' booklet. (Both booklets from the British Dyslexia Association.)