Searching for one keyword or phrase can mean your results are too vague and broad. If you search with several keywords, it’s a good idea to use more advanced search options, or to use some boolean operators. By doing this, your search will be more focussed and you will have fewer, but more accurate results to work with.
Try some of the suggestions on this page for more advanced searching and see what works for you and your topic.
University of Exeter students might like to use their Search Techniques LibGuide
Search techniques
Watch this brief video on search techniques or have a look at some below.
Remember there is no such thing as the perfect search!
Don't give up too easily and try different search terms and techniques to help you find what you need.
Try different search methods
Have a look at this video about snowball and citation searching which can help you move your research forward quickly.
Boolean Searching
Boolean operators are simple linking words.
These are: AND / OR / NOT
AND Narrows your search
Example:
crime AND poverty
Your results are limited to those that contain all your keywords
OR Broadens your search
Example:
college OR university
Your results will have either or both of your search terms
NOT Eliminates search terms
Example:
cloning NOT sheep
Your results will be narrower because you have eliminated certain words
Truncation and wildcards
Library databases can be fussy about the way you spell words, so if you aren’t sure of spelling you or if you know there are multiple variations of your search term, then use wildcards or truncation to cover all possibilities.
Truncation: expands your search to include different endings of a word
Example: theor* = theorist / theory / theory / theoretical / theorise
Wildcards: allow you to search for different spellings of a word by filling in the blank in the middle
Example: gr?y = grey / gray
It’s a good idea to check the Help options in databases as the type of wild card symbol used can vary!
Other advanced searching tips
Exact phrases
To find exact phrases i.e. with the words next to each other, you can sometimes use quotation marks. So to search for global warming as a term, type "global warming"
Grouping terms
You can try using brackets to group terms within a query to clarify the order of multiple operators.
Examples:
- Shakespeare AND (tragedy or sonnet)
- (Irish OR celtic) NOT gaelic
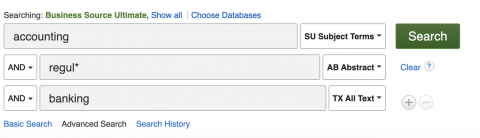
Field searching
In advanced search options in library databases or Library Search you can specify fields you'd like to search.
Common fields include:
- author
- title
- journal title
- abstract
- publisher
- date/year of publication
- subject/descriptor
You can combine multiple fields using the boolean AND, OR, NOT operators.
You can add lines for each concept of your topic and build a search string.
Example
For a more detailed look at field searching watch this video from Iowa State University
Have a look at the other pages in our Finding Information section to explore the different search tools and sources you might look at. In our academic databases page watch our video on when and why you might want to use digital collections.