Overview of dyspraxia
Dyspraxia (also known as Developmental Co-ordination Disorder) is characterised by difficulties with co-ordination, but it can also involve problems with organisation, memory, concentration and speech. The medical model of dyspraxia defines it as an impairment or immaturity of the organisation of movement. Associated with this, there may be problems of language, perception and thought. Dyspraxia often occurs with other SpLDs such as dyslexia, ADHD and autism.
Many people with dyspraxia also have strengths in areas such as creativity, determination and problem-solving.
Common challenges faced by students with dyspraxia
- Taking longer than peers to learn new skills and information.
- Organisation, time management and task prioritisation.
- Structuring written work and checking for spelling, punctuation and grammar mistakes.
- Balance and coordination.
- Processing and organising information.
- Fine motor skills affecting handwriting, typing, craft work, lab work, using apparatus and rulers, etc.
- Sense of direction, confusing left and right, map reading.
- Losing and forgetting things.
- Increased sensitivity to light, sound, smell, taste etc.
- The ability to screen out background noise during group discussions.
- Anxiety, depression and poor self-esteem.
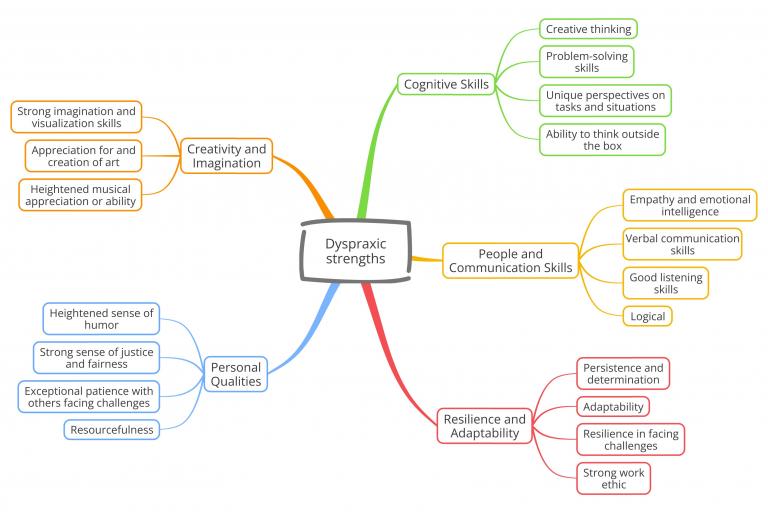
Strengths of dyspraxia
This mind map shows some common strengths of dyspraxic people. Remember, though, that every experience of dyspraxia is unique.
See also: 17 Famous People with Dyspraxia.

Adult Dyspraxia Questionniare
A quick, free tool to help you decide if you might benefit from further assessment.
For a pdf version, see this Adult Dyspraxia Checklist.
Wikipedia entry
A comprehensive entry on Developmental Coordination Disorder from Wikipedia (I know. I am sorry.)